Anesthesia and Reanimation
Anesthesia is the general name of various numbing methods and literally means numbness. In our hospital, anesthesia applications are performed by our anesthesia and reanimation specialists to ensure that patients do not feel pain and have a comfortable experience during surgical procedures. The type of anesthesia to be administered is determined by our specialist physicians and administered to the patient at the correct rates through anesthesia delivery systems, resulting in temporary loss of consciousness.
Anesthesia techniques, which have been used in the medical world for about 150 years and are constantly evolving, ensure that consciousness, reflexes and sensation are eliminated while maintaining the life functions of patients during surgical procedures. This is critical for both patient comfort and the surgeon's ability to work comfortably. Thanks to anesthesia, reflexes are suppressed and muscle relaxation is achieved during surgical intervention, which allows the operation to be performed more easily.
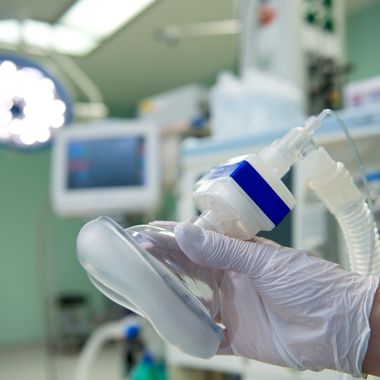



One of the main responsibilities of our anesthesiologists is to ensure the continuity of anesthesia during the surgical procedure and to safely terminate the effects of anesthesia after the procedure and wake the patient up.
At our hospital, we provide anesthesia services at the highest standards. With our expert anesthesia team and modern technological infrastructure, we aim to provide our patients with a safe and comfortable surgical experience.
For more information about our anesthesia services or to ask any questions, please contact us via [phone number] or [website].
Types of Anesthesia
General anesthesia is a type of anesthesia in which the patient is rendered completely unconscious and does not feel pain. It is ideal for major surgical procedures. Drugs are usually administered intravenously or by inhalation (breathing). With this method, the patient is completely asleep and feels nothing during the surgical procedure.
Regional anesthesia is a type of anesthesia in which a specific area of the body is numbed. The main types are as follows:
Spinal anesthesia: Anesthetic medication is injected into the spinal cavity to numb the lower body area. It is usually used for lower abdomen, pelvis and leg surgeries.
Epidural Anesthesia: Anesthetic medication is injected into the epidural space around the spinal cord to numb a large area. It is commonly used for pain control during childbirth and some surgical procedures.
Nerve Block: Anesthetic medication is injected around the nerves in a specific part of the body to block the pain sensation in that area. It is preferred for specific areas such as arms, legs or face.
Local anesthesia is a type of anesthesia in which a small area is numbed. It is often used for minor surgical procedures or dental treatments. The anesthetic drug is injected directly into the area to be treated, so that only the targeted area is numbed and the patient remains conscious.
Sedation is a type of anesthesia in which the patient is relaxed and painless but conscious. It is suitable for minor surgical procedures and endoscopic procedures. Sedation allows the patient to remain relaxed during the procedure and induces light drowsiness.

